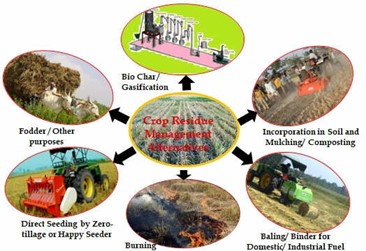
Crop residue management in Western Uttar Pradesh presents a unique set of challenges and opportunities due to the region's specific agricultural practices, cropping patterns, and environmental conditions. Situated in the fertile Gangetic plains, Western Uttar Pradesh is known for its intensive agriculture, characterized by the cultivation of crops like wheat, rice, sugarcane, and pulses. Effective management of crop residues in this region is crucial for sustaining soil fertility, enhancing crop productivity, and mitigating environmental degradation. One of the primary challenges in crop residue management in Western Uttar Pradesh is the prevalent practice of stubble burning, particularly after the harvest of rice and wheat crops. Stubble burning releases harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and posing serious health hazards. To address this issue, there is a growing emphasis on promoting alternative residue management practices such as mulching, incorporation, and crop residue-based biomass utilization.
Mulching, which involves spreading crop residues on the soil surface, helps conserve soil moisture, suppress weed growth, and improve soil structure. Farmers in Western Uttar Pradesh can adopt mulching techniques using crop residues from wheat and rice to cover the soil after harvest, reducing the need for burning. Incorporation of crop residues into the soil through tillage practices like plowing or discing can enhance soil organic matter content, nutrient cycling, and microbial activity. However, careful consideration of soil moisture, temperature, and crop rotation is essential to optimize the benefits of residue incorporation while minimizing soil erosion and compaction risks.
Furthermore, promoting the utilization of crop residues for bioenergy production, such as biomass briquettes or biogas generation, can provide an additional source of income for farmers while reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating greenhouse gas emissions.
In conclusion, sustainable crop residue management practices tailored to the specific needs and conditions of Western Uttar Pradesh are essential for ensuring the long-term viability of agriculture in the region. By adopting alternative residue management techniques and promoting resource-efficient farming practices, farmers can enhance soil health, mitigate environmental impacts, and contribute to sustainable agricultural development.